First WISE-Cities workshop at Marne-La-Vallee on 29 June 2018
Considering the need to move from a water paradigm to an urban environment paradigm, the WISE Cities project (Tremplin 2017 project proposal of i-site FUTURE) aims to study innovative technologies and practices pertaining to the water-energy-soil nexus. This multidisciplinary project gathers the following partners: CSTB, LEESU-Ecole des Ponts et Chaussées, ESIEE Paris and IFSTTAR and will concentrate first on two main case cities (Paris and Nantes) and two time horizons (2030 and 2050).
In 2018, the WISE Cities project received seed funding from i-site FUTURE in order to be further developed and re-submitted mid-October 2018 for a 4 year period.
In this context, the first WISE Cities workshop, was held on June 29th at ESIEE Paris (Marne-la-Vallée), aimed at bringing the project research community together to discuss key aspects as well as the advances of the project before the new deadline.
Renowned researchers from the Paris Interdisciplinary Energy Research Institute (LIED/PIERI) and the UMRAE from Nantes were invited to share their experience of interdisciplinary research crossing social and engineering sciences. These interventions highlighted the necessity of discussing interdisciplinary methods, problems and issues in the early phases of the project and to consider interdisciplinarity more as a working methodology, not limited to a specific task of the project. In these regards, it arose that a certain level of flexibility in vocabulary is needed for fruitful cross-disciplinary collaborations.
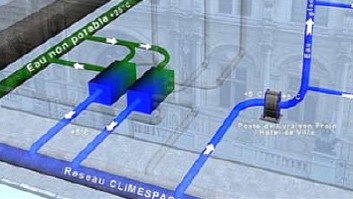
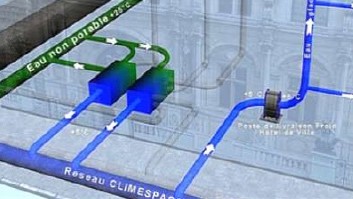
Example of WES interactions : (1) Cold recovery from water network

Example of WES interactions : (2) Green roof

Example of WES interactions : (3) Pavement watering
A specific session aimed at letting the different understandings of Water-Energy-Soil nexus emerge from participants, who were invited to answer the question “What is a WES innovation?” The results of the exercise - which has been analysed and integrated into the new version of the project - point out the core role of water as a driving element of the nexus. Furthermore, soil was clearly identified as generating the widest variety of meanings, ranging from real estate and property to a physical substrate for vegetation growth. Moreover, participants agreed that the WES nexus calls for a decentralized understanding of environmental resource management and a connection with societal visions and political choices.
Other topics were also discussed: approaches for scenario elaboration and deployment and the identified demonstrators where WES innovation will be tested in real-world conditions.
- Silvia Bruzzone, Leesu, ENPC
- Bernard de Gouvello, Leesu, ENPC
- Martin Hendel (ESIEE Paris/LIED)








 Scientific production
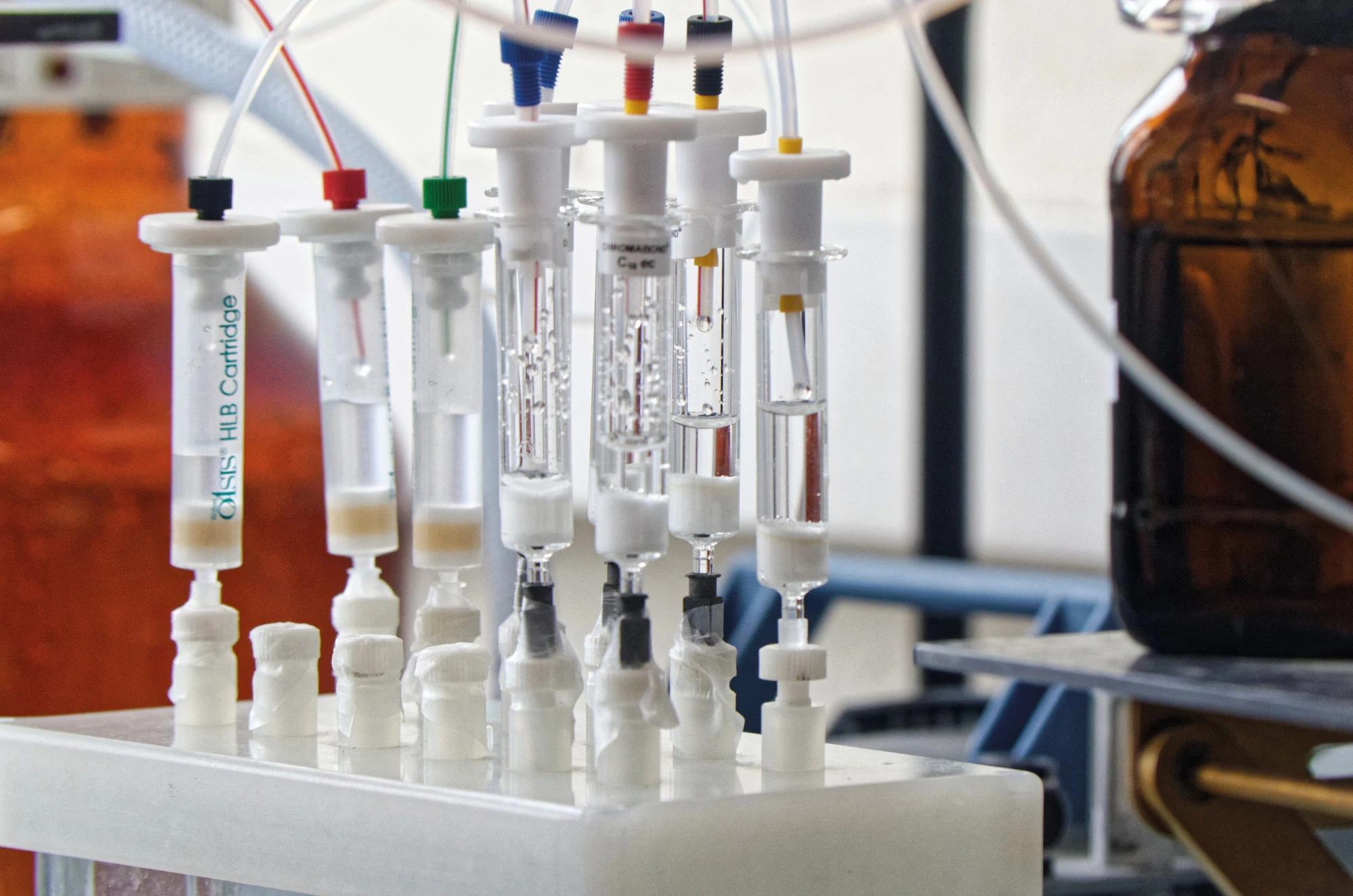
Scientific production Technical resources and equipment
Technical resources and equipment Expertise and disciplines
Expertise and disciplines