Recent publications
935.
- titre
- Assessing water quality restoration measures in Lake Pampulha (Brazil) through remote sensing imagery
- auteur
- Alexandre Assunção, Talita Silva, Lino de Carvalho, Brigitte Vinçon-Leite
- article
- Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2025, ⟨10.1007/s11356-025-35914-6⟩
- titre
- Do suspended particles matter for wastewater-based epidemiology?
- auteur
- Gauthier Bernier-Turpin, Régis Moilleron, Chloé Cenik, Fabrice Alliot, Sabrina Guérin-Rechdaoui, Thomas Thiebault
- article
- Water Research, In press, 280, pp.123543. ⟨10.1016/j.watres.2025.123543⟩
- titre
- Plastic debris dataset on the Seine riverbanks: up to 38 000 pre-production plastic pellets reported per square meter
- auteur
- Romain Tramoy, Laurent Colasse, Johnny Gasperi, Bruno Tassin
- article
- Data in Brief, 2025, pp.111735. ⟨10.1016/j.dib.2025.111735⟩
- titre
- La persistance des champs d’épandage d’eaux usées de l’agglomération parisienne au cours du second XXe siècle
- auteur
- Etienne Dufour
- article
- Métropolitiques, 2025, ⟨10.56698/metropolitiques.2174⟩
- titre
- Stock and vertical distribution of microplastics and tire and road wear particles into the soils of a high-traffic roadside biofiltration swale
- auteur
- Max Beaurepaire, Tiago de Oliveira, Johnny Gasperi, Romain Tramoy, Mohamed Saad, Bruno Tassin, Rachid Dris
- article
- Environmental Pollution, 2025, 373, pp.126092. ⟨10.1016/j.envpol.2025.126092⟩
Roulepur project
published on , updated on
Summary presentation of Roulepur research project
Duration : 2014 - 2019
Title : Innovative solutions for the sustainable management of road runoff contamination
Project acronym : Roulepur
Lutte Contre les Micropolluants dans les Eaux Urbaines : 2014 call for research projects by ONEMA, Water Agencies and MEDDE Ministry
Partners
- 3 research institutions :
- Ecole de Ponts ParisTech – LEESU
- CEREMA – DTerIF
- Univ. Bordeaux – UMR EPOC
- 3 local authorities :
- Ville de Paris
- CG 93
- CG 77
- 2 companies :
- St Dizier Environnement
- Ecovegetal
Contact : Marie-Christine GROMAIRE
Context
- Runoff from roadways and parking lots
- A complex matrix of micropollutants
- Need for source control / treatment
- Necessity to adapt the solutions to site specifics
Objectives
- Diagnose the composition and toxicity of runoff water, identifying primary sources
- Evaluate several innovative treatment solutions in situ in terms of efficiency (hydrology, chemistry and ecotoxicity) and sustainability (maintenance, aging)
- Analyse the overall environmental performance through a life cycle assessment (LCA)
- Assess solutions’ ownership conditions (social, technical and economic) and diffusion potential within the local context
Study sites
- 4 sites in Paris conurbation
- Contrasted pollution levels and urban contexts
- 4 treatment facilities
- Both nature-based and technological devices
- Vegetative filter strip and biofiltration swale
- Pervious, vegetated car park
- Small, horizontal sand filter
- Compact settling / filtration / adsorption device
- Permeable filtering parking developped by Ecovégétal (Broué et Villeneuve le Roi)
 Ecovégétal
Ecovégétal
- Non-infiltrating horizontal planted filters (CG93 – Rosny sous Bois)
- Vegetated shoulders + filtering / infiltrating ditches (CG77 – RD212 Compans)
- Compact decantation / filtration / adsorption device from STOPPOL 10CKF (Ville de Paris, voie George Pompidou)
 Saint-Dizier Environnement
Saint-Dizier Environnement
Methodology
- A holistic and multidisciplinary approach
- Micropollutants studied
- Diagnosis of road runoff contamination
- Targeted screening: PBDE, DEHP, organotins, nickel, HBCDD, PFOS, benzotriazoles, tetrabromobisphenol A, platinoïdes
- Non targeted screening
- Performance evaluation of facilities
- SS, POC, DOC, N, P, major ions, Hydrocarbons
- Micropolluants: 12 metals, PAH, alkylphenols, bisphenolA, phtalates
- Toxicity analysis
- Diagnosis of road runoff contamination
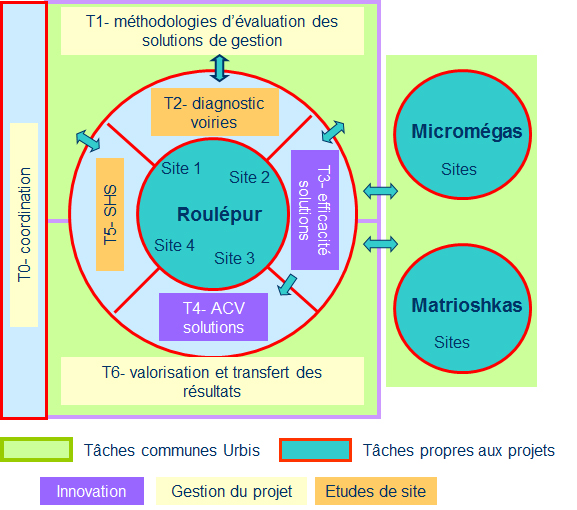
Tasks
- T1. Assessment methodologies of management systems
- T2. Monitor water composition and toxicity - Identify primary sources
- T3. Evaluate in-situ the effectiveness of several innovative treatment solutions of different technicalities (hydrology, chemistry and ecotox)
- T4. Analyze the global environmental performance (LCA) and the sustainability (maintenance, aging) of these solutions
- T5.Evaluate social and technical acceptability, cost, potential for diffusion of solutions
- T6. Valorisation and transfer of results









 Scientific production
Scientific production Technical resources and equipment
Technical resources and equipment Expertise and disciplines
Expertise and disciplines





